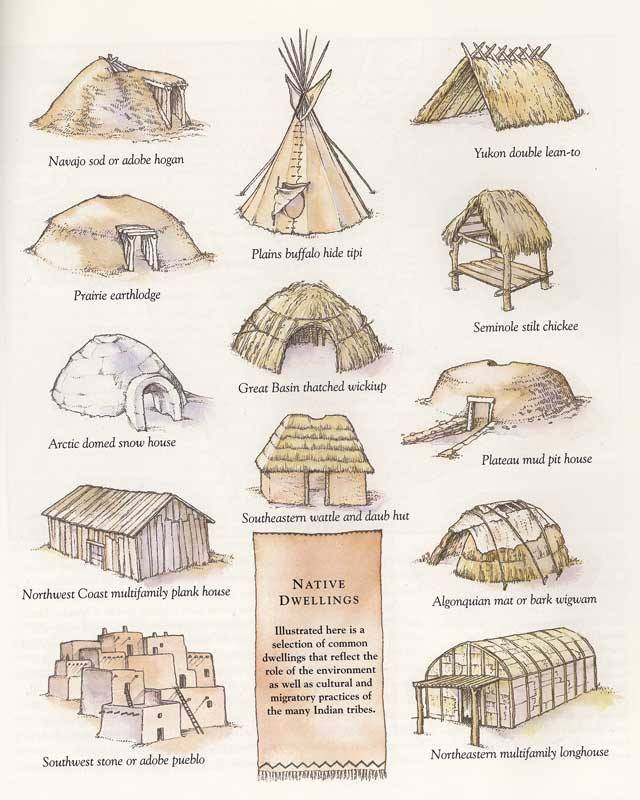
| by Jamie K. Oxendine, Lumbee/Creek Contributing Author for The Gathering PRELUDE Native Americans from the Atlantic to the Pacific and the Arctic to the Tropics were quite cordial and rather kind to guests in the home. Europeans and later Americans noticed certain mannerisms concerning a guest at home that was far beyond their own concept of providing hospitality. Even after the massive persecution from both Europeans and later Americans the indigenous people of North America were still quite benevolent to each other and even the White Man when it came to having guests in the house. Here are some very general policies that were common among many Tribes across Native America. One must remember that these are not set in stone and are not laws as there were vast differences among all Native American Nations. THE ETERNAL COOKING MEAL Among the Eastern Woodland Peoples it was common to always have a large container of food on or near the lodge fire. In the North East this container was usually a very large calabash (gourd) or wood bowl kept simmering via hot stones and full of some kind of food stew. This was typically a stew of meat or fish with vegetables. When one was obliged they would partake of the stew and eat. The stew was retained by always replacing what had been taken. For example if a piece of meat or fish was removed a piece of meat or fish was added. If stock was removed then water and other fillers or thickeners was added and so forth. Among the South East Nations a large earthen clay container of hominy (grits) was always available on the fire in a lodge and some dried or smoked meat or fish was also kept nearby. For many Native American Nations there was no set meal time. Whenever one was hungry they dipped in the containers and had something to eat. This was often referred to as The Eternal Cooking Meal as described by Europeans and later Americans. After White Contact the original containers were replaced with metal trade goods of iron, tin, brass and copper. Guests were always fed. In fact the normal greeting for guests was not “Hello” or “How are you doing” or even “Good to see you” it was always “Have you eaten?” Even in the leanest of times it was the duty of the clans/families to do their best to keep The Eternal Cooking Meal. One can easily assume that this was very hard to do in a bitter winter or a very dry summer yet it amazed the White Man that the accumulating, conserving, storage and distribution of food stuffs by Native Americans during very sparse times was nothing more than remarkable. BEING POLITE IN THE LODGE From the Longhouses and Wigwams of the Northeast to the Adobes of the Southwest and from the temporary Igloos of the Artic to the Open Lodges of the Southeast as well as from the Tipis of the Great Plains to the Cedar Plank Houses of the Northwest, there was a certain accommodating protocol of life in the home of all Native Americans. This decorum did vary greatly from Nation to Nation and Tribe to Tribe and even Clan to Clan but there was a general set of what one might call “Mutual Consideration” or “Common Courtesy” or just better yet plain old “Civility” and “Good Manners.” HOST OBLIGATIONS
GUEST RESPONSIBILITIES
GOOD MANNERS FOR ALL
CONCLUSION Europeans and later some Americans knew of some of the mannerisms above as all cultures have very specific rules of etiquette for being civil. But for various reasons such decent behavior had become lost among the European explorers and later colonists when meeting new and different cultures. Such respect also vanished among the later American colonists and settlers pushing ever more across North America. Unfortunately assimilation, removal, relocation, and more assimilation of Native Americans created a massive injury to the well-practiced lodge etiquette for all peoples of Native America. Sad but many of the courtesies of the Native American Culture that was developed over centuries are not always found among Native Americans today. It is not surprising to find The Native American People not treating each other with veneration. In fact the opposite is quite true and one does not need to do a study or research of the phenomenon. All one needs to do is step back and witness the poor treatment and disdain that some Native Peoples have towards each other. It is for this reason that we must all seek wisdom from Elders and those of proper knowledge and use the most basic of common understanding to be kind to each other regardless of culture and history. Remember, esteem and reverence starts in the home and is passed on from there to others. BIBLIOGRAPHY Carver, Jonathan. 1778. Travels Through the Interior Parts of North America, In the Years 1766, 1767, 1768. London. Hudson, Charles. 1976. The Southeastern Indians. University of Tennessee Press. Lawson, John. 1967. A New Voyage to Carolina. University of North Carolina Press. Lewis, Meriwether. 1814. (Reprint 1904). History of the Expedition of Captains Lewis and Clark, 1804-5-6. Chicago: A.C. McClurg. McKenney, Thomas & Hall, James. 1933. The Indian Tribes of North America. Edinburgh: John Grant. Mails, Thomas. 1972. Mystic Warrios of the Plains. New York: Doubleday & Company. Mails, Thomas. 1973. Dog Soldiers, Bear Men and Buffalo Women. NJ: Prentice Hall. Richter, Daniel, K. 1992. The Ordeal of the Longhouse: The Peoples of the Iroquois League in the Era of European Colonization. University of North Carolina Press. Tanner, John & Edwin, James. 1830. (Reprint 2007). A Narrative Of The Captivity And Adventures Of John Tanner, U. S. Interpreter At The Saut De Ste. Marie During Thirty Years Residence Among The Indians In The Interior Of North America. Whitefish, MT: Kessinger Publishing. Timberlake, Henry, Lt. 1765. (Reprint 2007). The Memoirs of Lt. Henry Timberlake: The Story of a Soldier, Adventurer, and Emissary to the Cherokees, 1756-1765. Cherokee, NC: Museum of the Cherokee Press William, Bertram. 1791. Travels Through North & South Carolina, Georgia, East & West Florida, the Cherokee Country, the Extensive Territories of the Muscogulges, or Creek Confederacy, and the Countryof the Choctaws; Containing An Account of the Soil and Natural Productions of Those Regions, Together with Observations on the Manners of the Indians. Philadelphia. Read more: http://www.powwows.com/2014/08/10/native-american-home-etiquette/#ixzz3bJ03Z2ek | About the Author: Contributing Author for The Gathering Editor, PowWows.com Director, Black Swamp InterTribal Foundation Native American Historian Remember, esteem and reverence starts in the home and is passed on from there to others. |
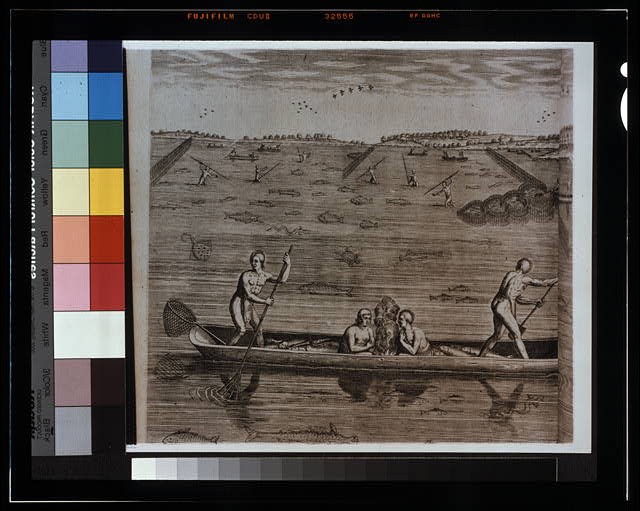
Year 1500s Virginia Indians Cooking Fish - Men may Dress Differently Now, but They still Like to BBQ5/29/2015
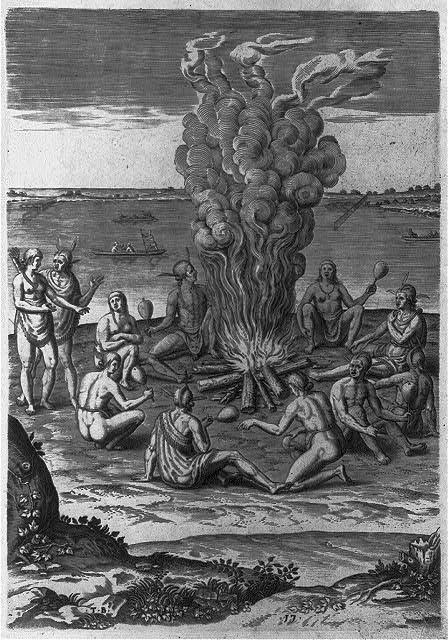
Library of Congress Title: "Praying around the fire with rattles" Summary: Group of Indigenous people of Virginia gathered around a campfire, some appear to be holding rattles; dugout canoes on river in background.
|
The index table below shows various events that we have offered over the years.
Embrace the Spirit
Interest Topics
All
Archives
May 2024
|




















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed